 |
SyterKit 0.4.0.x
SyterKit is a bare-metal framework
|
 |
SyterKit 0.4.0.x
SyterKit is a bare-metal framework
|
#include <io.h>#include <stdarg.h>#include <stdbool.h>#include <stddef.h>#include <stdint.h>#include <types.h>#include <sys-clk.h>#include <sys-gpio.h>#include <sys-spi.h>#include <log.h>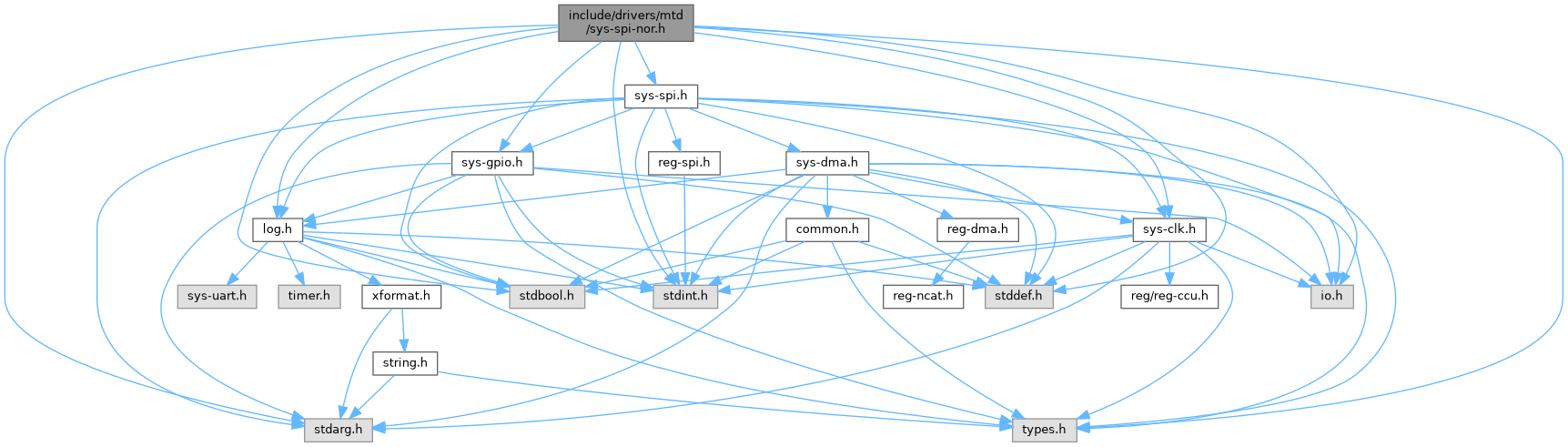
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | sfdp_header |
| struct | sfdp_parameter_header |
| struct | sfdp_basic_table |
| struct | sfdp |
| struct | spi_nor_info |
Macros | |
| #define | SFDP_MAX_NPH (6) |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct sfdp_header | sfdp_header_t |
| typedef struct sfdp_parameter_header | sfdp_parameter_header_t |
| typedef struct sfdp_basic_table | sfdp_basic_table_t |
| typedef struct sfdp | sfdp_t |
| typedef struct spi_nor_info | spi_nor_info_t |
Enumerations | |
| enum | SPI_NOR_OPS { NOR_OPCODE_SFDP = 0x5a , NOR_OPCODE_RDID = 0x9f , NOR_OPCODE_WRSR = 0x01 , NOR_OPCODE_RDSR = 0x05 , NOR_OPCODE_WREN = 0x06 , NOR_OPCODE_READ = 0x03 , NOR_OPCODE_PROG = 0x02 , NOR_OPCODE_E4K = 0x20 , NOR_OPCODE_E32K = 0x52 , NOR_OPCODE_E64K = 0xd8 , NOR_OPCODE_ENTER_4B = 0xb7 , NOR_OPCODE_EXIT_4B = 0xe9 } |
| Enumeration of SPI NOR Flash operation opcodes. More... | |
| enum | SPI_CMD_OPS { SPI_CMD_END = 0x00 , SPI_CMD_INIT = 0x01 , SPI_CMD_SELECT = 0x02 , SPI_CMD_DESELECT = 0x03 , SPI_CMD_FAST = 0x04 , SPI_CMD_TXBUF = 0x05 , SPI_CMD_RXBUF = 0x06 , SPI_CMD_SPINOR_WAIT = 0x07 , SPI_CMD_SPINAND_WAIT = 0x08 } |
| Enumeration of SPI command operations. More... | |
Functions | |
| int | spi_nor_detect (sunxi_spi_t *spi) |
| Detects the presence of an SPI NOR flash chip. | |
| uint32_t | spi_nor_read_block (sunxi_spi_t *spi, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t blk_no, uint32_t blk_cnt) |
| Reads a block or multiple blocks of data from the SPI NAND flash memory. | |
| uint32_t | spi_nor_read (sunxi_spi_t *spi, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t addr, uint32_t rxlen) |
| Reads data from the SPI NOR flash memory. | |
| #define SFDP_MAX_NPH (6) |
| typedef struct sfdp_basic_table sfdp_basic_table_t |
| typedef struct sfdp_header sfdp_header_t |
| typedef struct sfdp_parameter_header sfdp_parameter_header_t |
| typedef struct spi_nor_info spi_nor_info_t |
| enum SPI_CMD_OPS |
Enumeration of SPI command operations.
This enumeration defines a set of commands used to control the behavior of SPI operations. These commands may include initialization, selection, deselection, and data transmission commands to facilitate communication with peripheral devices.
| enum SPI_NOR_OPS |
Enumeration of SPI NOR Flash operation opcodes.
This enumeration defines the opcodes used for various operations on SPI NOR Flash memory. Each opcode corresponds to a specific command that can be issued to the NOR Flash for performing read, write, erase, and other operational tasks.
| int spi_nor_detect | ( | sunxi_spi_t * | spi | ) |
Detects the presence of an SPI NOR flash chip.
This function attempts to identify and initialize the SPI NOR flash chip connected to the specified SPI interface. It resets the chip, waits for it to be ready, and retrieves its information. If successful, it logs the chip ID and its capacity.
| [in] | spi | Pointer to the SPI interface structure. This should be initialized and configured before calling this function. |
-1 if no supported SPI NOR chip is found.
The function performs the following steps:
| uint32_t spi_nor_read | ( | sunxi_spi_t * | spi, |
| uint8_t * | buf, | ||
| uint32_t | addr, | ||
| uint32_t | rxlen | ||
| ) |
Reads data from the SPI NOR flash memory.
This function reads a specified length of data from a given address in the SPI NOR flash memory into a provided buffer. The reading is performed in blocks, and it handles cases where the read address is not aligned to the block size.
| [in] | spi | Pointer to the SPI interface structure. |
| [out] | buf | Pointer to the buffer where the read data will be stored. |
| [in] | addr | The starting address from which to read data in the SPI NOR. |
| [in] | rxlen | The number of bytes to read from the SPI NOR. |
rxlen if an error occurs or if the end of the memory space is reached.The function first checks if the read address is misaligned with the block size. If so, it reads a partial block. Then, it reads as many complete blocks as possible before potentially reading another partial block at the end.
| uint32_t spi_nor_read_block | ( | sunxi_spi_t * | spi, |
| uint8_t * | buf, | ||
| uint32_t | blk_no, | ||
| uint32_t | blk_cnt | ||
| ) |
Reads a block or multiple blocks of data from the SPI NAND flash memory.
This function reads one or more contiguous blocks from the SPI NAND flash memory into a provided buffer. It handles reading the data in chunks defined by the read granularity and performs the necessary address calculations to handle multiple blocks.
| [in] | spi | Pointer to the SPI interface structure. |
| [out] | buf | Pointer to the buffer where the read data will be stored. |
| [in] | blk_no | The starting block number from which to read data. |
| [in] | blk_cnt | The number of blocks to read from the SPI NAND. |
The function reads data from the SPI NAND flash memory in chunks based on the configured read granularity (info.read_granularity). It waits for the SPI bus to be ready before each read operation. The function will continue reading until the requested number of blocks has been fetched. If the data to be read exceeds the maximum read length (0x7FFFFFFF bytes), it adjusts the size of each read operation accordingly.